CEDRA-AVsandTM
Wastewater and Storm Sewer Modeling
CEDRA-AVsandTM enables the engineer
to create the spatial geometric model of a storm water, wastewater
or combined system, impose storm water and/or wastewater loads,
and apply custom peaking factors to average daily contributions.
Open channel and closed conduit flows may be computed, system
adequacy determined, flow hydrographs generated and stage-storage
curves developed. Over thirty (30) built-in conduit shapes are
available as well as the ability to define user-specific pipe
shapes. In addition, the engineer has the ability to perform a
backwater analysis and produce computational reports and engineering
plots for review or inclusion in a report. CEDRA AVsandTM offers the engineer an ArcView®
GIS and ArcGIS® interface to (a) the SEWERSTM
modeler of CEDRA SANDTM and
(b) the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's SWMMTM modeler, thereby integrating modeling
and GIS technology. Version 4.31 and 4.4h of SWMM are supported.
CEDRA AVsandTM can also be used
to satisfy U.S.E.P.A. CMOM requirements for determining system
adequacy. CEDRA-AVsand, in conjunction with the CEDRA-Skeletization
extension, provides functionality to compute the maximum capacity
within a series of pipes. In the CEDRA-AVsand software, a group
of pipes connected in series is referred to as a “strip”.
By determining a strip’s maximum capacity, the engineer is
able to identify which manholes within a strip should be bolted
when (a) the upstream most manhole of a strip is full, and (b)
the depth of water at the downstream most manhole, or outlet structure
is known. A formal report containing the results of the strip
capacity analysis can be generated, as well as, a profile showing
the strip capacity energy grade line.
In addition to the modeling tools, CEDRA AVsandTM
provides functionality for editing attribute data using customized
dialog boxes. The CEDRA-DataEditorTM extension, which is included with CEDRA
AVsand, enables the user to identify the specific themes and attributes
which the user can edit. Quality control and data verification
tools are included with the CEDRA-DataEditor extension to ensure
that the database is properly maintained. The customized dialog
boxes, which the user defines, are established without having
the user write any Avenue, Visual Basic or other programming language
software. With a simple point and click, CEDRA DataEditor users
are able to edit and maintain their tabular information without
having to start and stop table editing sessions.
CEDRA AVsand when utilized with any of CEDRA's geometry software, CEDRA AVcad, CEDRA AVcogo, CEDRA AVland or CEDRA AVparcel, provides the user a package that integrates Modeling, Mapping, Data Maintenance and GIS in a single common desktop environment. As such, the need to move data from one software environment to another is eliminated because ArcView is used as the common desktop environment. CEDRA AVsand users are able to begin and end projects entirely in ArcView.
ArcGIS users should check out the CEDRA-ArcView3-Tools toolbar. This toolbar offers a number of selection tools which will increase productivity by at least 30%. This is accomplished by reducing the number of clicks that are made in performing typical selection operations. ArcGIS users who have previously worked with ArcView GIS will definitely appreciate these tools.
To download an order form for a demo version of CEDRA-AVcad with Tutorial Manual click on the link. Once the order form has been downloaded, fill-in the requested information at the bottom of the form and then fax, e-mail or mail the order form back to The CEDRA Corporation. To see what's included in the demo version of the software click here CEDRA Demo Pack Information.
Those interested in a lot more functionality for just a little
more expense should check out the CEDRA-AGsuite
software package.
Click on this link for a color brochure,
which can be viewed and/or printed with Adobe Acrobat® ReaderTM.
|
|
|
|
CEDRA AVsandTM
CEDRA AVsandTM is fully compatible with Versions 3.0, 3.1, 3.2 and 3.3 of ArcView® GIS and Versions 9.3, 10.0, 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4, 10.5, 10.6 and 10.7 of ArcGIS®.
CEDRA AVsandTM provides the following functionality:
Building the database from within AVsandTM
- Define the geometric configuration (service areas, nodes
and pipes):
- in an interactive graphics environment, or
- by importing:
- node and pipe shapefiles,
- an Arc/Info coverage, or
- a CAD drawing followed by using a
- Wizard to establish the model from the imported data.
- Establish the materials inventory.
- Introduce storm water and/or wastewater loads with:
- Direct flow rates.
- Inflow Hydrographs.
- Land parcel and/or building foot print polygon association.
- Support of a variety of coordinate systems such as State Plane, UTM, latitudes-longitudes, etc.
- Ability to specify measures in feet, meters, varas, chains, rods, etc.
- Ability to create, edit and maintain attribute data with the CEDRA-DataEditorTM extension.
- Ability to automatically assign sequential node/pipe numbers for optimum modeling performance.
- Ability to customize the material codes and their annotation strings.
Geometric functionality
- Includes and expands CEDRA AVcadTM.
- Automatic polygon creation using auto-search (tracing) functionality.
- Individual point, line, circular arc and spiral definition.
- Point and line traversing.
- Tangent line and curve generation.
- Ability to insert, delete and relocate vertices of a polyline or polygon.
- Specification of angles in decimal or degrees/minutes/seconds form.
- Specification of angles as an Azimuth, Bearing or Cartesian direction.
- Point Snapping across themes.
Database query and editing
- Hydraulic computational results.
- Inventory features.
- Operational and historic data.
- Maintain inventory and hydraulic attributes.
- Precise geometric location.
- Ability to break a pipe.
- Modeling control and other parameters.
- Storm and waste contributions.
- Interactively edit node and pipe attributes.
- Interactively edit inflow hydrographs, individually or by applying an equation to alter the flows in mass.
- Ability to skeletonize a model to reduce the number of pipes.
Hydraulic modeling
- Storm, sanitary, combined and infiltration.
- Closed and open conduit system.
- Compute loads based upon Land Use polygons and Consumption factors.
- Static and dynamic modeling using:
- Rational Method - Manning's Equation under full flow or maximum flow conditions or,
- St. Venant equations using an explicit solution technique to step forward in time.
- System capacity and Backwater analysis.
- Strip capacity analysis and report generation.
- Siphons, diversions, parallel pipes and loops.
- Flow hydrograph and detention routing.
- Over 30 built-in, and custom pipes shapes.
- Ability to customize the recommended pipe size list.
- SAND, SWMM - 4.31 and SWMM - 4.4h interfaces.
- Ability to produce fully annotated profiles with customized
parameter settings with the ability of:
- specifying desired horizontal and vertical scales,
- specifying desired grid lower and upper datum values,
- specifying desired starting and ending station values,
- specifying desired horizontal and vertical intermediate and heavy grid line intervals,
- including the energy grade and/or strip capacity grade lines,
- including the backwater water elevation, and
- specifying whether the profile is to be drawn in a left to right or right to left direction.
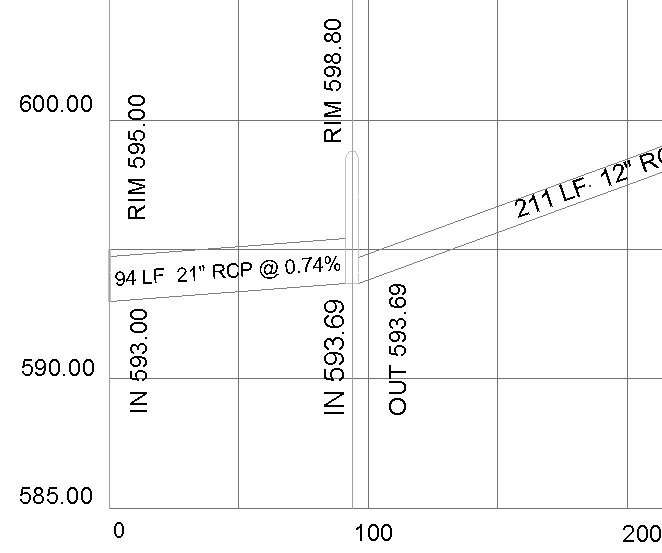
- Ability to produce fully annotated profiles for report and plan and profile inclusion (click on the link to see a sample).
Importing functionality
- Waste and storm contribution data.
- dBase, Info, SDE and ASCII files may be directly read.
- Access, Paradox, FoxPro, Oracle, Sybase, Informix, DB2, Ingres
by:
- Exporting to dBase or ASCII for direct reading or,
- accessing through ODBC - Open Database Connectivity.
- any ODBC/SQL-compliant database.
- Import of PC Arc/Info coverages, Arc/Info coverages and libraries.
- Direct reading of Shapefiles.
- DXF, DWG, DGN and CEDRA CAD drawings.
- VPF, MapInfo, Atlas GIS and ASCII map data.
- Ability to have comments within the ASCII files that are processed for mass importing.
- Ability to mass import polygons from an ASCII file.
- Ability to mass import points in a variety of formats from an ASCII file.
- Ability to mass import lines that are defined by node numbers from an ASCII file.
- Ability to mass import polylines that are defined by a line ID value and vertex coordinates from an ASCII file.
- Ability to import a CEDRA "COGO" file which is
an ASCII file that allows the user to mass import:
- Lines given a direction and a distance.
- Polygons given a direction and a distance for each course (side) comprising the polygon. The polygons may also contain curves (simple, compound and reverse) rather than just straight line sides.
- Non-Tangent Curves given a chord direction, a chord length and a radius.
- Tangent Curves given a chord length and a radius.
- Tangent Curves given an arc length and a radius.
- Tangent Curves given a central angle and a radius.
- Ability to display the following raster file formats:
- TIFF (.tif files).
- ERDAS (Rev 7.3 and 7.4 .lan and .gis files).
- IMAGINE (.img files).
- BSQ, BIL and BIP.
- Sun Rasterfiles (.rs, .ras, and .sun files).
- BMP.
- JPEG (.jpg files).
- IMAGINE (.img files).
- Arc/Info GRID.
- RLC (Run-Length Compressed format).
Exporting functionality
- Ability to export features (points,
lines, polygons and annotation) as an Arc/Info Generate File.
- In the form of a single Generate file, or
- As multiple Generate files using the layer name as the name of the file.
- Ability to export features (points,
lines and polygons) in the form of a Vertex Coordinate File.
- In the form of X,Y coordinates,
- In the form of North,East coordinates,
- In the form of Longitude,Latitude coordinates, or
- In the form of Latitude,Longitude coordinates.
- Ability to export features (points, and multi-points) in a variety of ASCII based formats.
- Ability to export features (points, lines, polygons and annotation) in the form of a DXF File.
- Ability to export features (polylines and polygons) adhering to the Traverse File Format.
Graphic display and/or reports
- Hydraulic and quality charts and tables.
- Flow hydrograph generation.
- Conduit and energy grade line profiles.
- Annotation of pipes and nodes.
- CAD functionality.
- Advance or return to previous views.
- Ability to save and assign a name to an unlimited number of views.
- Ability to return to a previous view by specifying a view name.
- Ability to zoom in or out of a view by specifying a scale factor.
- Individual and global text scaling.
- Individual and global text editing.
- Viewing of ASCII based files.
- Customized selection tools for ArcGIS users.
- Ability to modify a specific attribute of one or more graphic text elements without altering any of their other attributes.
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Printing Capability for ArcGIS
ArcGIS® users have the ability to print the active data
frame using the Print Data Frame command, which is available in
the CEDRA-DataFrame-Tools toolbar. The Print Data Frame command
differs from conventional ArcGIS printing in that the user is
able to control: (a) the map scale, (b) the map area to be printed,
(c) the location of the map on the paper and (d) optionally, whether
a data frame, which contains a map sheet border, should be included
or not in the map.
As most ArcMap users have realized, within an ArcMap document
file (.mxd) all data frames share the same layout. This causes
the difficulty of when the layout view is activated all of the
data frames in the document file appear in the layout, which for
some applications is not what the user wants. The Print Data Frame
command will print the active data frame, from data or layout
view, ensuring that: (a) the desired map scale is preserved, and
(b) all other data frames do not appear on the plot. This is achieved
by programmatically positioning all data frames, other than the
active data frame, in the document file outside of the user specified
sheet limits (Paper Size parameters). In so doing, when the layout
view is activated the only data frame that appears in the layout
view is the active data frame.
This capability allows the user to have a single document file
that contains many data frames with each data frame containing
a complete drawing sheet. Without the Print Data Frame command
the user would have to: (a) create separate document files for
each drawing sheet or (b) manually reposition all data frames,
other than the active data frame, outside of the sheet limits.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In addition, users have the ability to operate in another mode
of map preparation. The first mode, which was described above,
is when a single data frame contains the entire map to be printed.
The second mode is where one data frame contains the map contents,
while another data frame contains the map border (title block,
sheet border, etc.).
The Print Data Frame command accommodates this scenario by providing
the Include Data Frame matching the Paper Size option.
When this option is checked the Print Data Frame command will
position the active data frame according to the specifications
in the Data Frame Size and Position parameters area and will include
in the plot the data frame whose name is either 11"x17",
24"x36" or Custom, depending upon which Paper Size is
active. This approach enables the user to create a single map
border, placing it in a data frame using one of the following;
11"x17", 24"x36" or Custom
as the name of the data frame, and generate multiple maps without
having to load the map border into multiple data frames.
DXF Export Capability for ArcView GIS and ArcGIS
ArcView® GIS and ArcGIS® users have the ability to create a DXF file, from within ArcView 3.x or ArcMap, for all visible features in the current map. Unlike other DXF export utilities, which process only one theme at a time, the CEDRA DxfExportTM extension processes all visible themes (shapefiles, personal geodatabases, enterprise geodatabases and coverages) in the current map. In addition, the CEDRA DxfExport utility will process annotation features and graphic text elements. As such, a DXF file created by this utility can include features and text. In processing the visible layers in the map:
- If a theme has selected features then only the selected features will be processed, if there are no selected features then all features in the theme will be processed, this includes point, polyline and polygon features. If the option Export Features displayed in the Current Extent is selected then all visible features in the current view will be exported regardless of the feature's selection state.
- If a theme has labels, the labels will need to be converted into annotation, using the Convert Labels to Annotation... command, in order for the labels to be exported. The labels that are converted can be stored either in a personal geodatabase or in the map, depending upon the user's preference.
- If there are selected MARKER, PEN, FILL and/or TEXT graphic
elements then these graphic elements will be processed (if the
user desires). If the view does not contain any selected graphic
elements then no graphic elements will be processed. In exporting
graphic elements note the following:
- All of the selected Marker elements will be placed in a layer called GrapMrkr,
- All of the selected Pen elements will be placed in a layer called GrapPen,
- All of the selected Fill elements will be placed in a layer called GrapFill, and
- All of the selected Graphic Text elements will be placed in a layer called GrapText.
- The name of the theme will serve as the name of a layer in the DXF file.
- Non-alphanumeric characters in a theme name are converted to the underscore character (_).
- The user has the ability to select one or more attributes, from a choice box that appears in the Create DXF File dialog box, for inclusion in the DXF file, if desired. When exporting attributes, the selected attributes will appear as "blocks" in the DXF file. These blocks will appear at the midpoint of the feature and the name of the block will be B_xxxx, where xxxx denotes the name of the layer the feature resides in. All of the attributes associated with the block will be listed vertically, one under the other. The ability to export attributes is important because: (a) it enables the user to transfer non-graphic information (attributes) into the DXF file, maintaining the association of the non-graphic information with the feature and (b) provides a mechanism for the user to maintain symbology and line styles. Regarding the latter, symbology and line styles, in the GIS classifications are based upon attributes, by exporting the attributes which the classifications are based upon, the user has the ability to regenerate the classifications in the system in which the DXF file is being read into. This, of course, is dependent upon the software which is reading the DXF file, that it has the ability to change symbology and line style using information that is stored in a "block".
| ArcMap - CEDRA-DxfExport Dialog Box |
|
|
As can be seen by examining the dialog box above, the user is able to:
- Control the name of the DXF file that is created. The Browse... button enables the user to use a standard file navigation dialog box to control the folder where the DXF file will be written to, as well as the name of the DXF file.
- Specify whether the theme names are to be trimmed to 8 characters or not. If a check appears in the square to the left of this parameter, the names of the visible themes that are processed will be trimmed to a maximum of 8 characters. The first 8 characters of the theme name will be used.
- Specify whether selected graphic elements are to be included in the DXF file creation. If a check appears in the square to the left of this parameter any graphic elements that are selected will be included in the creation of the DXF file.
- Specify whether a DXF file for importing into the CEDRA I-series software is to be created or not.
- Specify which attributes if any are to be included in the DXF file as "blocks". If a check appears in the square to the left of this parameter all attributes which are selected in the choice box will be included in the DXF file as "blocks". There is no limit to the number of attributes that can be selected, and
- Specify whether the visible features in the current extent (view) are to be processed. If a check appears in the square to the left of this parameter then the only features that will be exported will be the visible features in the current extent, regardless of their selection state. In addition, if the Export Selected Graphics (Marker, Pen, Fill and Text) option is selected, all Marker, Pen, Fill and Graphic Text elements in the visible annotation group layers which are within the current extent will be exported, regardless of their selection state. The name of the annotation group layer will serve as the name of the layer these graphic elements are placed in.
- Specify whether the data that is exported is to appear in the same coordinate system as the current view (data frame) or not. If this option is not checked, the data that is exported will be in the coordinate system of the theme's (layer's) source data. If this option is checked, all data that is exported will be in the same coordinate system as currently displayed in the data frame.
- Specify whether features are to be clipped to the current map display extent when exporting from Data View. If this option is not checked, if any portion of a feature falls within the current map display extent, the entire feature will be exported. If this option is checked, the feature will be clipped to the current map display extent prior to exporting.
- Specify whether polyline and polygon features are to be exported as LWPolyline AutoCAD entities. If this option is checked, all polyline and polygon features will be exported as a LWPolyline entity, rather than a Polyline or Polygon entity. If a polyline forms a closed figure then a closed LWPolyline entity will be exported.
ArcView 3.x Tools for ArcGIS
ArcGIS users who have worked with ArcView GIS will notice that the commands shown below: (a) do not operate the same in ArcMap as they did in ArcView or (b) are just not a part of core ArcGIS. These commands did not provide GIS functionality but they were an essential part of how ArcView GIS users operated in the ArcView 3.x environment. To ease the transition to ArcGIS, CEDRA's ArcGIS based software includes the CEDRA-ArcView3 Tools toolbar. This toolbar enables ArcGIS users to interact with ArcMap in a manner similar to how ArcView GIS users operated in the ArcView 3.x environment. For users who have never worked with ArcView GIS, these tools provide an easier and more flexible means of interacting with the map.
| CEDRA-ArcView3 Tools toolbar |
|
|
Functionality offered in the CEDRA-ArcView3 Tools toolbar
- Identify features from the active layers in the Table of Contents.
- Select features from the active layers in the Table of Contents.
- De-select or clear the selected features from the active layers in the Table of Contents.
- Zoom to the extent of all layers in the Table of Contents.
- Zoom to the extent of the active layers in the Table of Contents.
- Zoom to the extent of the selected features in the active layers in the Table of Contents.
- Make all layers in the Table of Contents visible.
- Make all layers in the Table of Contents invisible.
- Delete the selected features in the map with a single click eliminating the need to (a) start the Editor, (b) select the appropriate dataset and (c) select the delete command.
- Delete a group of vertices in a selected polyline or polygon feature by defining a rectangle that encloses the vertices to be deleted.
- Open the attribute table for the selected layer(s) and/or table(s).
- Switch or reverse the selection set for the selected layer(s) and/or table(s).
- Set the current active layer (Target Layer) by picking the desired layer from an alphabetically sorted list of layer names and clicking the OK button.
To download a color brochure, which can be viewed and/or printed with Adobe Acrobat® ReaderTM, click on the following link CEDRA Software Information.
CEDRA-AVsand is licensed as per the terms of the CEDRA Software License Agreement.